The Challenge
The Solution
Role
Senior UX/UI Designer
Project Management
Agile Scrum Methodology
Tools
Figma, Workshops and Adobe Anlytics, Crazy Egg
The Process
To address the challenge, I adopted the Double Diamond process model, a proven framework for solving complex design challenges.
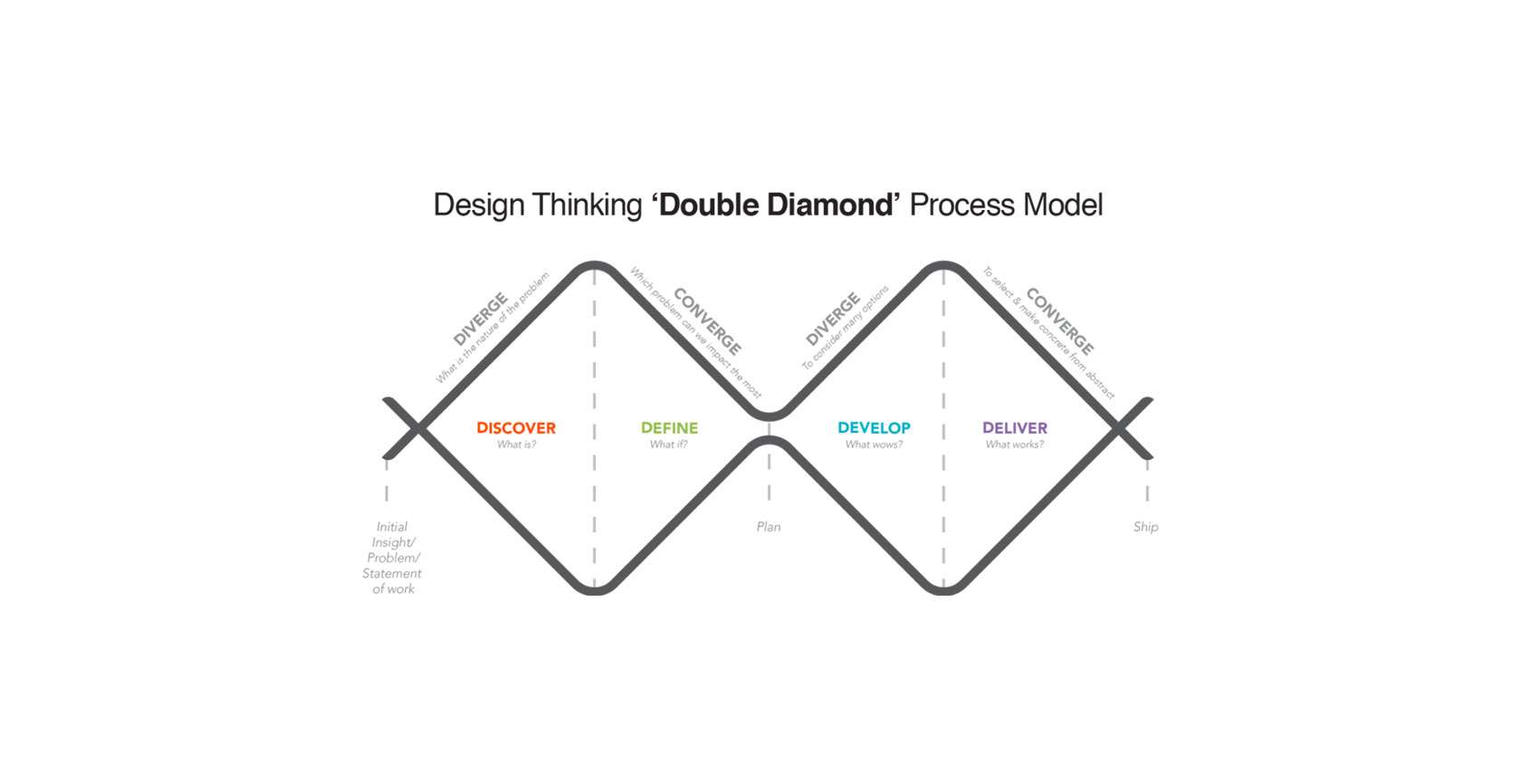
Discovery
During the Discovery phase, we ran multiple workshop sessions with stakeholders and team members to uncover pain points and priorities. We analyzed Adobe Analytics to understand customer click-through patterns and identify which areas of the navigation were being used—or ignored. Additionally, we leveraged Crazy Egg heatmaps to observe user interactions, uncovering engagement trends and friction points. These insights provided a clear picture of customer behaviour and informed data-driven decisions for restructuring the navigation.
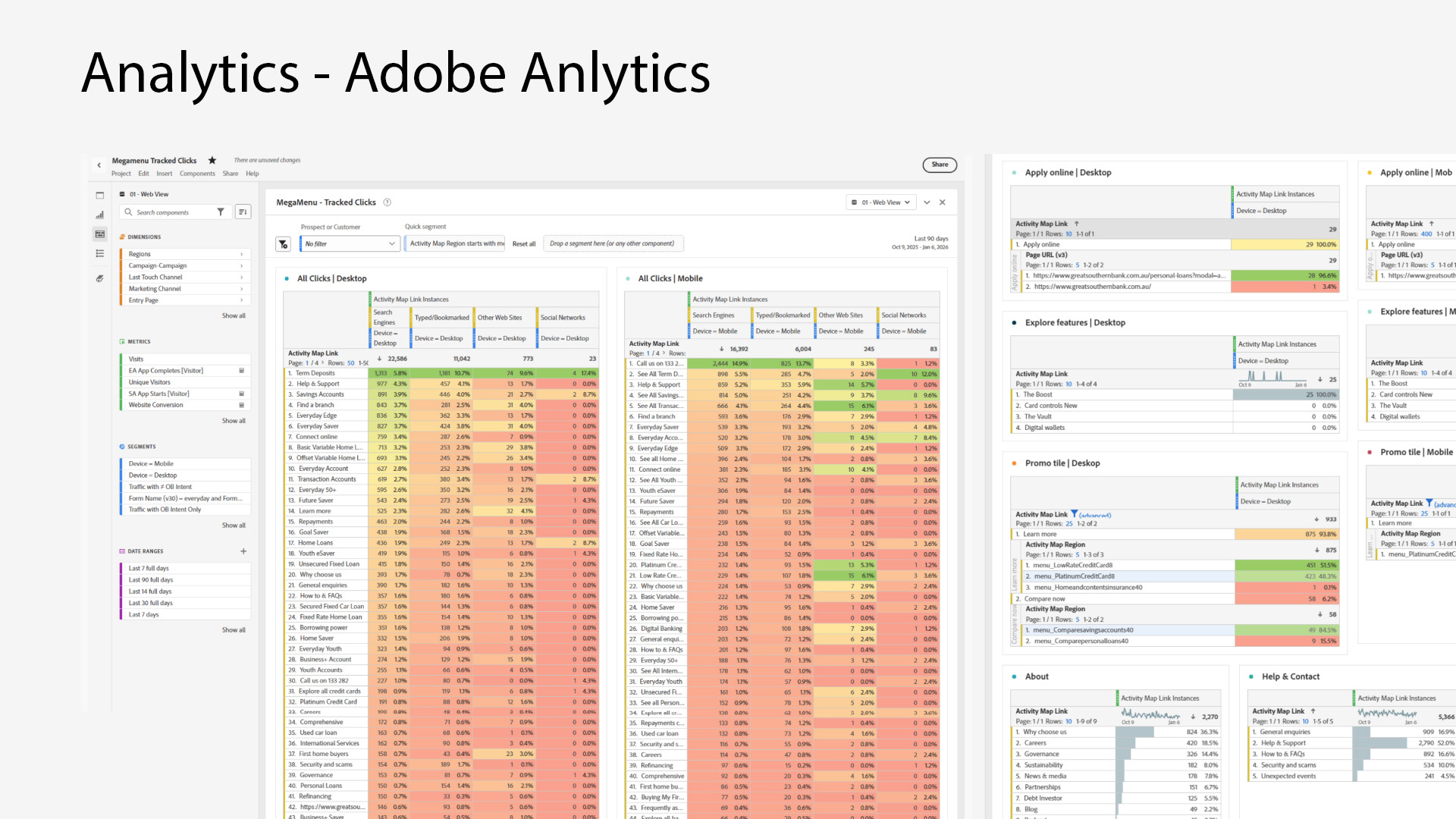
Adobe analytics information gathering
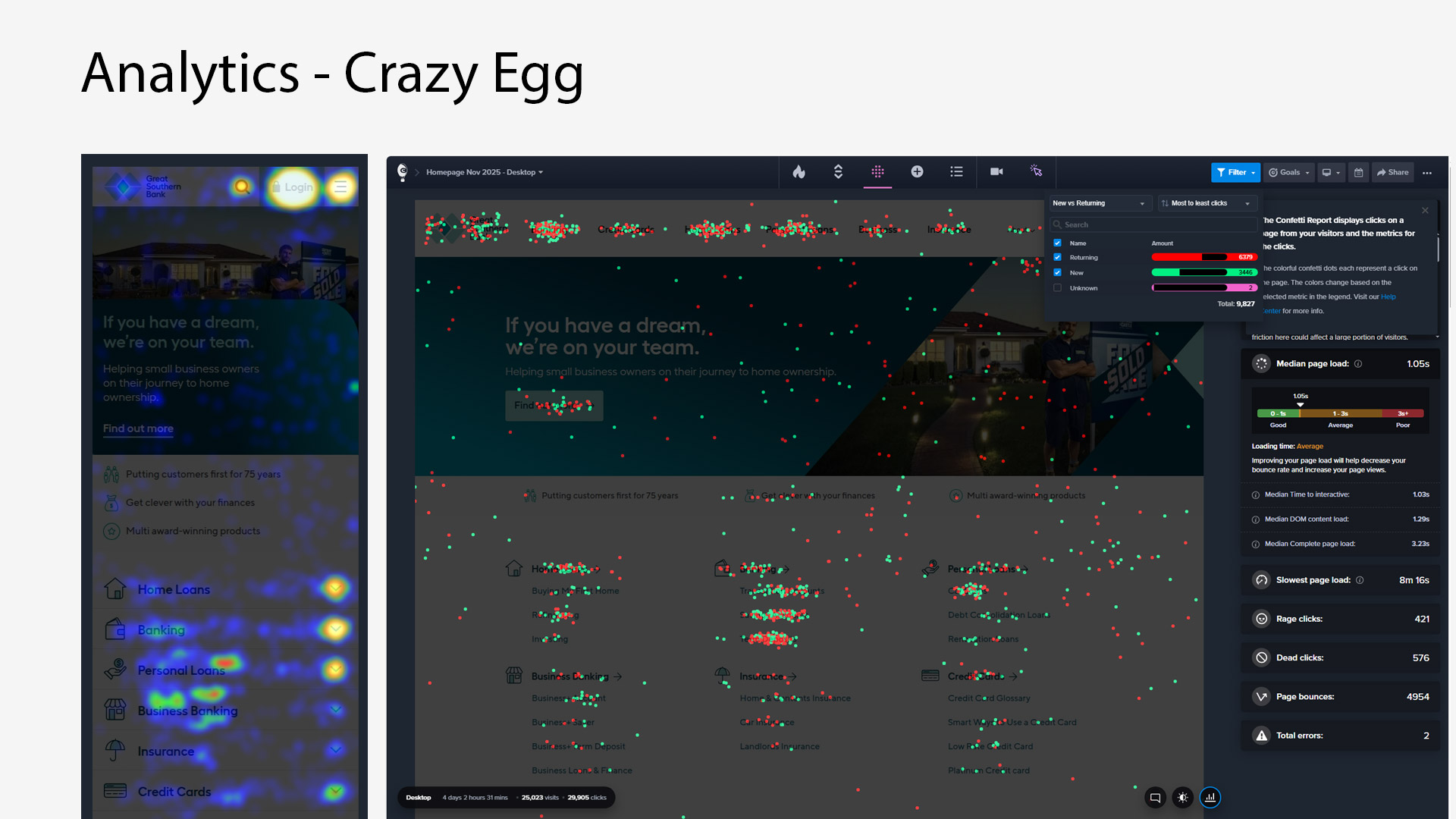
Crazy egg analytics information gathering

Indepth Analysis of GSB navigation
Consolidation
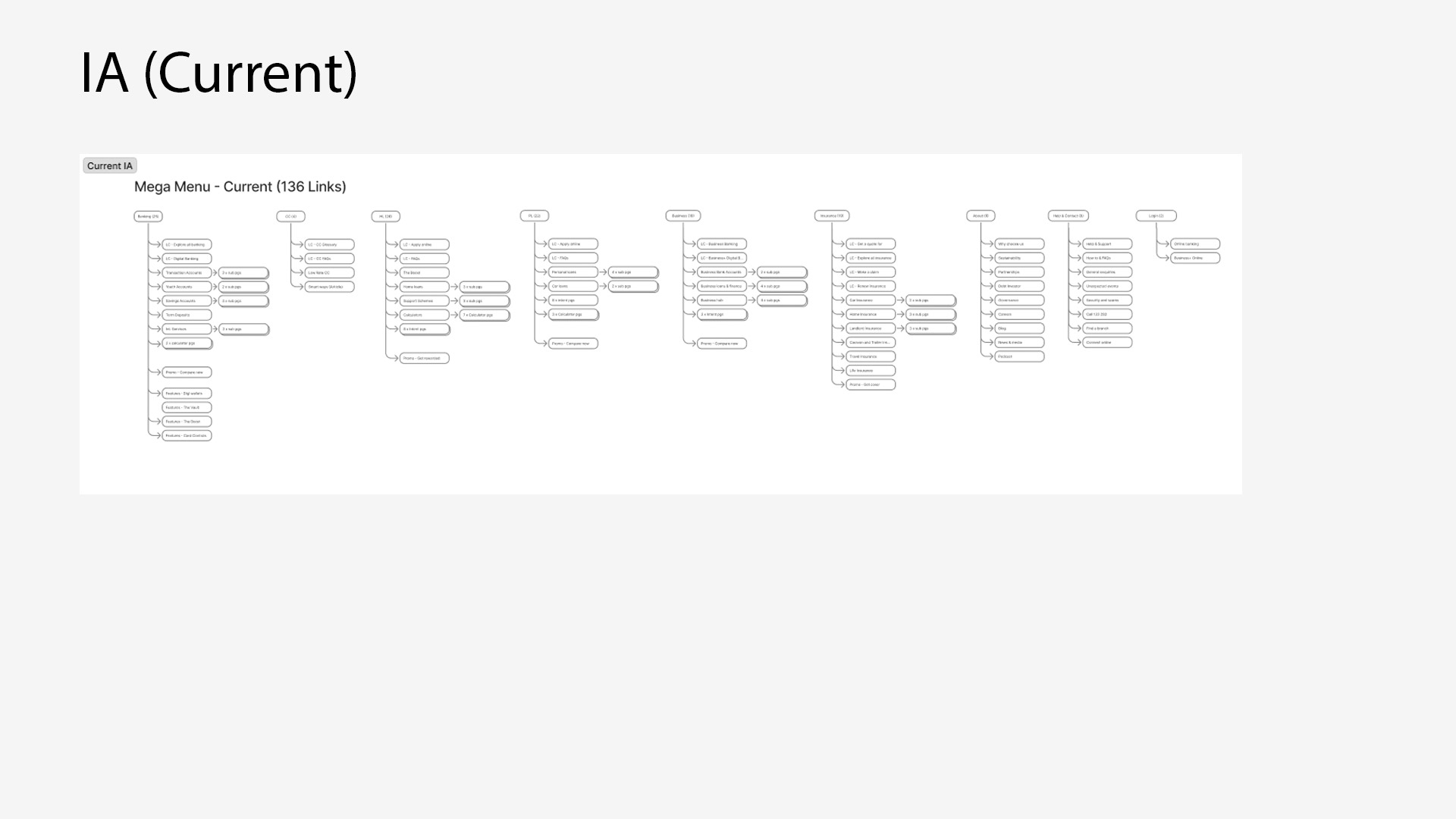
IA mapping of current navigation
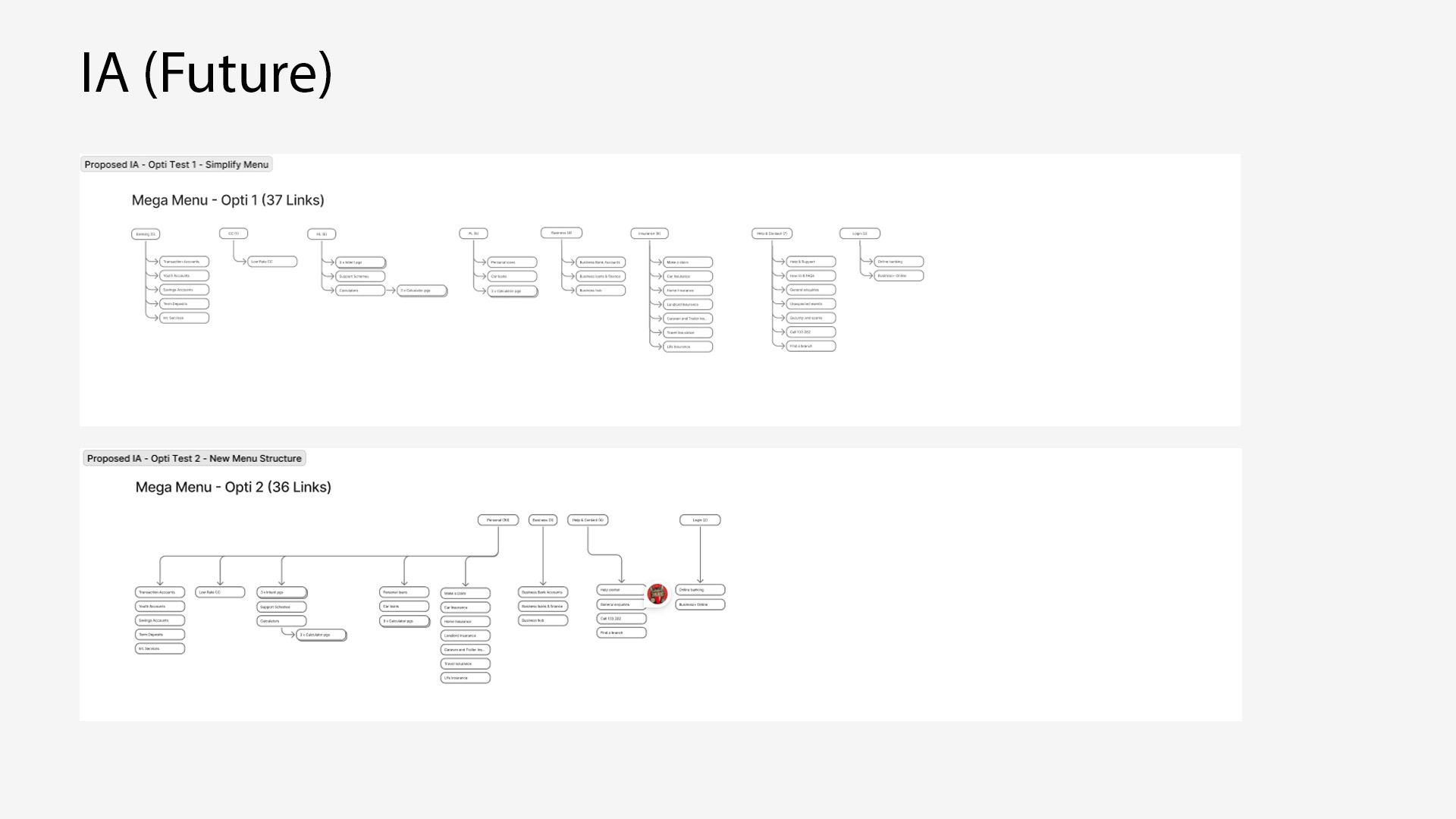
IA recommendation for experiments
Experimentation
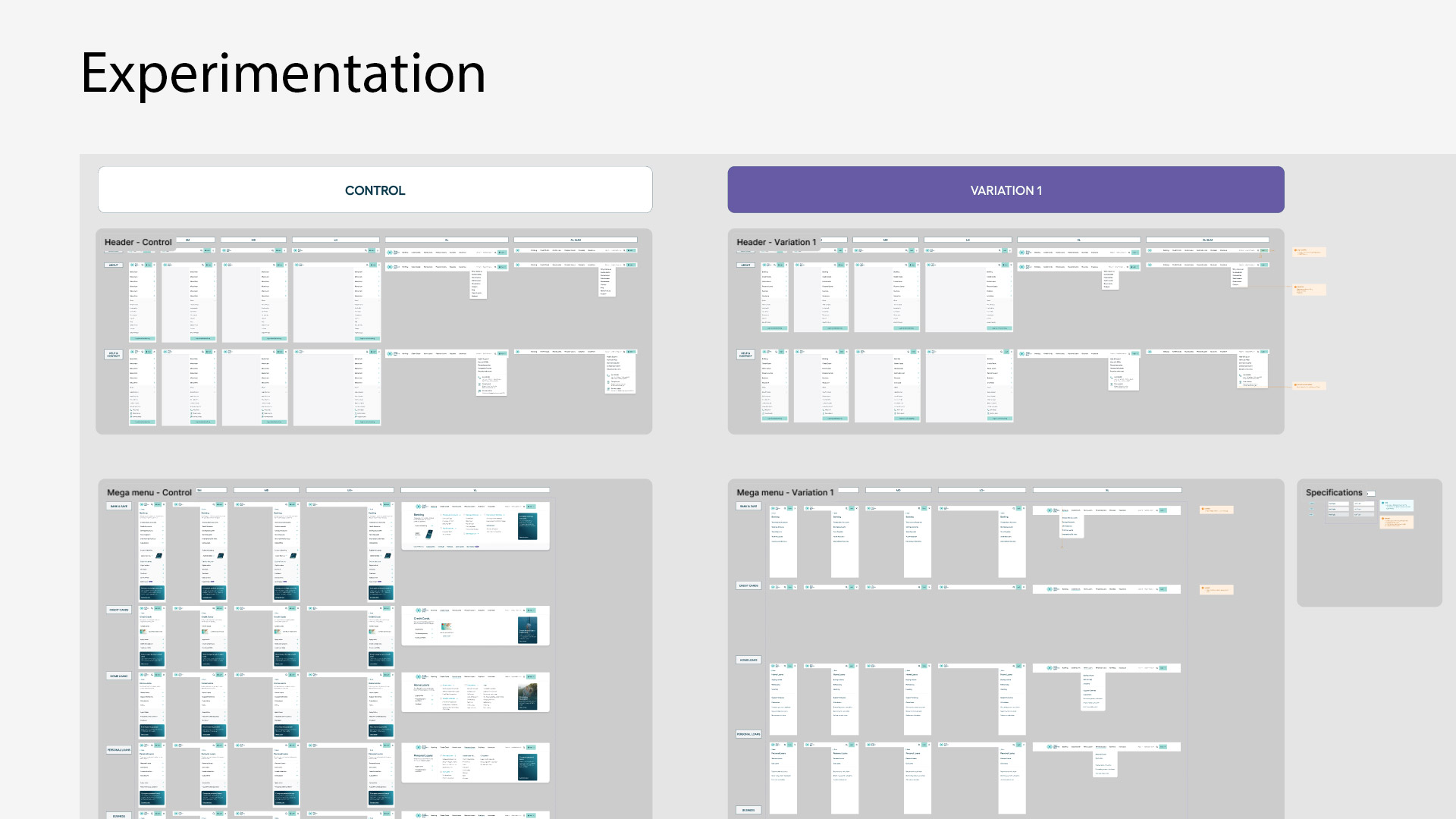
Control vs Variation 1
